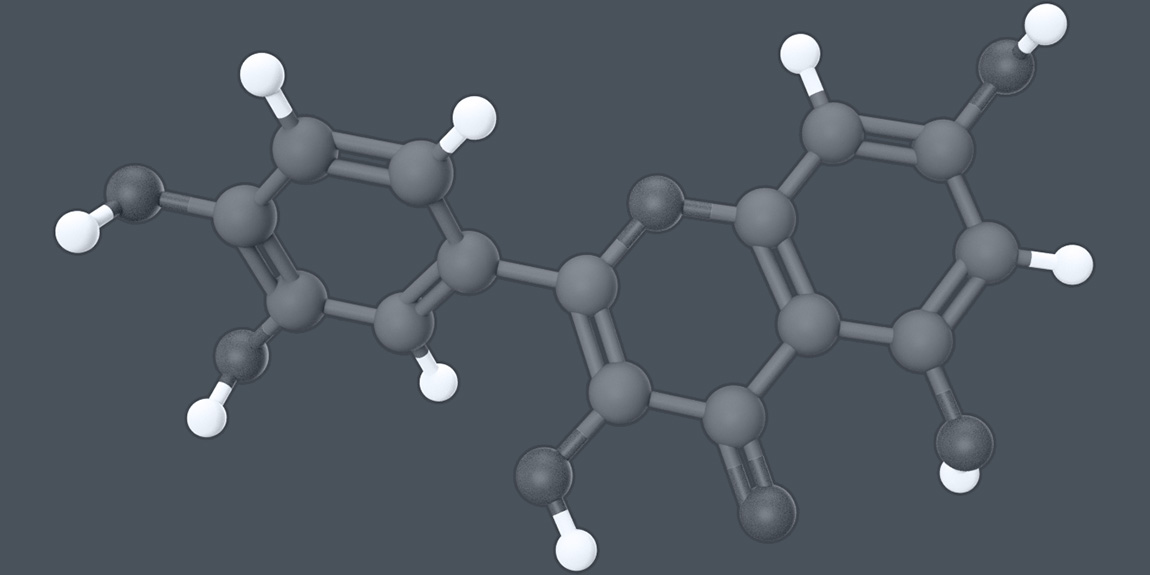
Quercetin is a pigment, plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. Quercetin is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains – apples, onions, parsley, berries, red wine, green tea, and other. Quercetin is one of the most abundant flavonoids in the diet and the most extensively studied one. Quercetin is a safe, natural antioxidant and can be used in human food and animal feed.
Numerous studies have shown that quercetin has a wide range of biological actions, such as anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, renoprotective, and antiviral. Quercetin can also attenuate lipid peroxidation, platelet aggregation and capillary permeability.
Quercetin has broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties and can be used in the treatment and prevention of serious infectious bacterial diseases and reduce the use of antibiotics.
H – ingredient has HIGH impact on specified disease
M – ingredient has MEDIUM impact on specified disease
N – there is no data confirming the impact of the ingredient on specified disease